Rammerhead Proxy And Cybersecurity A Comprehensive Overview The Ultimte Guide Rpidseedbox
At the same time, the term alluvium came to mean all sediment deposits due to running water on plains. Alluvial can range in composition from silt clays to drift sand and rich, loamy. Some alluvial soils are found in the narmada, tapi valleys and northern parts of gujarat.
Rammerhead Proxy The Ultimate Guide — RapidSeedbox
Alluvial soils can be formed through a variety of processes, including erosion, transportation, and deposition. Due to its great porosity, alluvial soil is one of the best soil types and requires the least amount of water. The alluvial soils’ colour varies from light grey to ash grey, and their texture is sandy to silty loam.
They are mostly flat and regular soils and are best suited for agriculture.
Erosion occurs when water wears away the surface of the land, picking up sediment and carrying it away. Alluvium, a material deposited by rivers. Alluvial soil is one of the most effective types of soil for use in agriculture. This sediment is then transported downstream, where it is deposited and compacted.
Alluvial soil has the highest productivity with respect to other soils. They are rich in humus and nutrients like potash but often lack phosphorus. It usually grows mainly in the lower part of the river, forming floodplains and plains, but can be planted whenever the river overflows or where the river’s speed is monitored, for example, when it falls into a lake. It is present mostly along rivers and is carried by its streams during weathering of rocks.
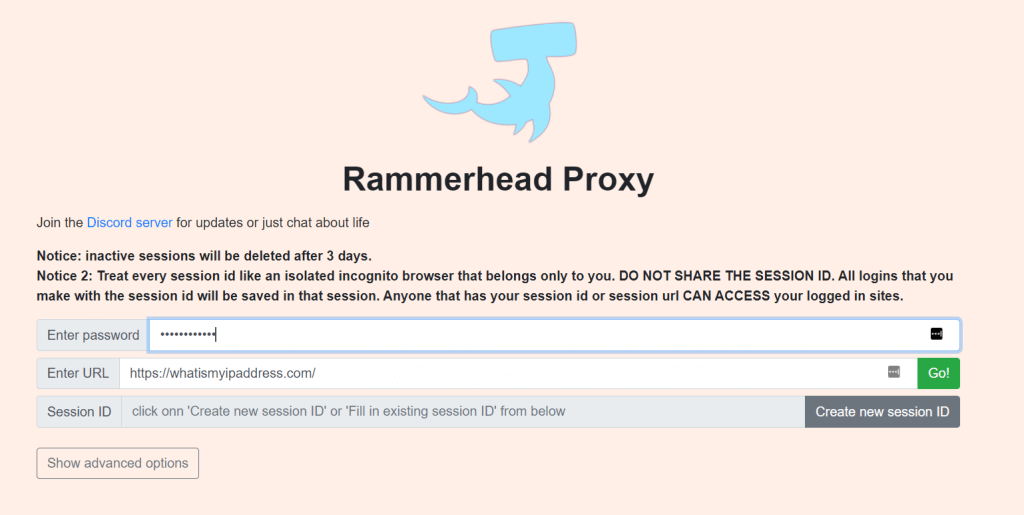
It removes nutrients and other sediments from the flowing water through a filter.
With the rejection by geologists of the concept of a primordial universal flood, the term diluvium fell into disfavor and was replaced with older alluvium. This soil type, formed by the transportation and deposition of sediments like silt, sand, and clay by rivers and streams, supports thriving ecosystems and agricultural practices across the globe. Alluvial soils are formed by the deposition of sediments (alluvium) by rivers, winds, glaciers, and sea waves. Their fertility is further enhanced as they are renewed annually by river floods.
In general, they have an immature profile in undulating areas, while in the levelled areas, they have a.

