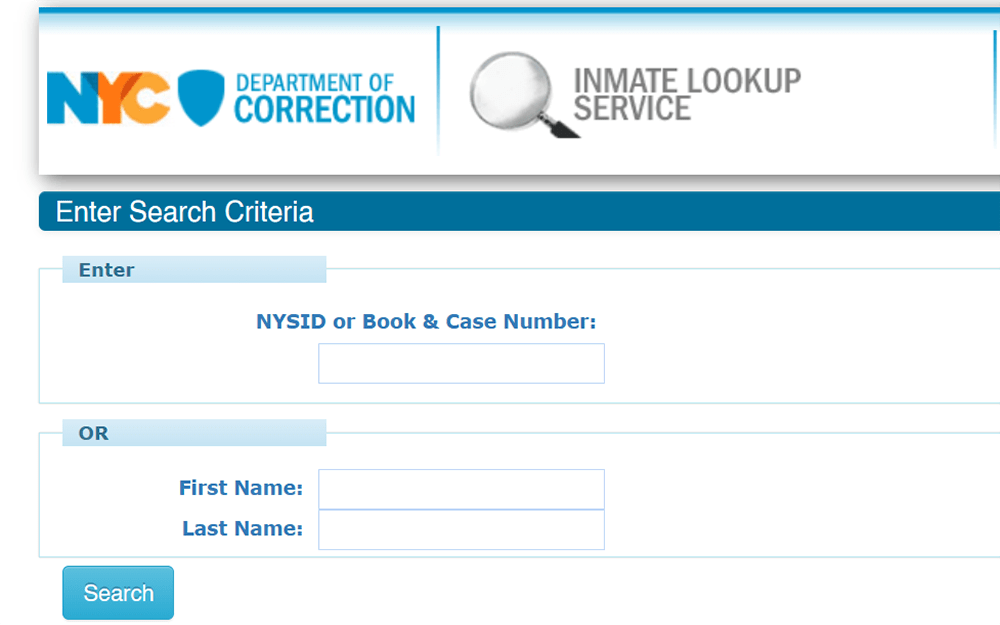
Nys Inmate Lookup Is It Safe And Secure Rikers L Service
These agreements are typically used to. One notable risk is counterparty risk. Explore the essentials of interest rate swaps, including their components, valuation methods, and risk management strategies.
New York Inmate Search Department of Corrections Lookup Prison
Though participants in the interest rate swap market often measure their exposure to the default of their counterparty, default risk is not the only material risk. Overview of interest rate swap agreement how does it work? One party makes fixed rate payments on an agreed hypothetical principal amount (“notional amount”), during a given.
But if one of the two parties.
Discover how interest rate swaps help mitigate financial risks in volatile markets. Swap agreements are financial contracts between two parties that involve the exchange of cash flows. Interest rate swaps offer benefits such as risk management, cost reduction, and flexibility. Because the parties involved are typically large companies or financial institutions, counterparty risk is usually relatively low.
The primary risk associated with interest rate swaps is counterparty risk, which is the risk that one party in the swap agreement may default on its obligation to make payments. However, they also expose parties to risks such as interest rate risk, counterparty. If an interest rate swap is entered into to hedge interest rate risk under a bond issue or a loan agreement,.